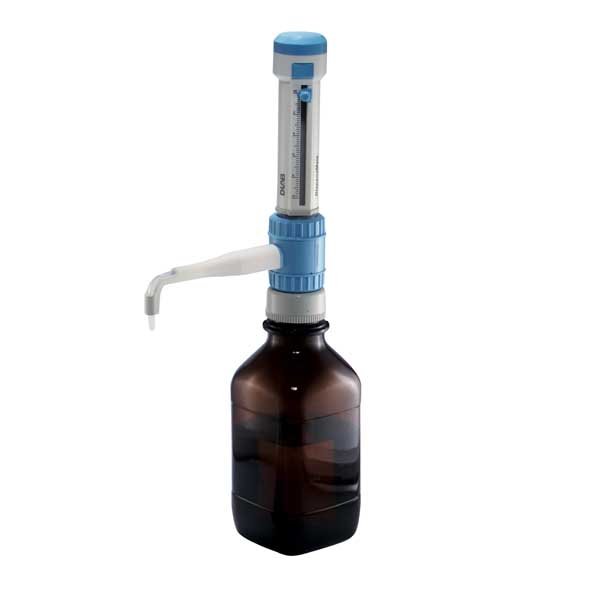
• Excellent chemical resistance, components are made of PTFE, FEP, BSG, PP
• Fully autoclavable at 121℃
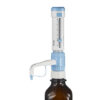
• Four ranges of bottle-top dispenser covering a volume range from 0.5mL to 50mL
• Easy for cleaning and maintenance
• The optional flexible discharge tube with safety handle permits fast and precise dispensing
• Vapor pressure max. 500mbar, viscosity max. 500mm2/s,
• Fully autoclavable at 121℃
• Four ranges of bottle-top dispenser covering a volume range from 0.5mL to 50mL
• Easy for cleaning and maintenance
• The optional flexible discharge tube with safety handle permits fast and precise dispensing
• Vapor pressure max. 500mbar, viscosity max. 500mm2/s,
• temperature max. 40oC, density max. 2.2g/cm3
• Dispensemate is supplied with S40, GL32, GL38,GL25, GL28
• Dispensemate is supplied with S40, GL32, GL38,GL25, GL28
| Cat.No. | Volume Range | Graduation | A≤± | CV≤ | ||
| ml | ml | % | μl | % | μl | |
| 7032100001 | 0.5-5 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 25 | 0.2 | 10 |
| 7032100002 | 1.0-10 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 50 | 0.2 | 20 |
| 7032100003 | 2.5-25 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 125 | 0.2 | 50 |
| 7032100004 | 5.0-50 | 1 | 0.5 | 250 | 0.2 | 100 |
Chemical resistance table:
| DispensMate Chemical Compatibility at 20℃ | |||||
| The parts of DLAB DispensMate which are exposed to liquid consist of BSG, PTEF, FEP. The material of closure | |||||
| cap of outlet is PP. The parts which have no access to liquid consist of PC and other materials. Please notice the | |||||
| table is merely a general guide, not a commitment from the manufacturer. Please read the user manual carefully | |||||
| before use and to do related experiments to determine whether a certain chemical should be used. For good | |||||
| laboratory practice, rinse out the liquid handing unit at the end of each day with distilled water to remove corrosive | |||||
| liquids. | |||||
| Reagent | Compatible | Reagent | Compatible | Reagent | Compatible |
| Acetaldehyde | + | Cyclohexane | Mineral oil (Engine oil) | + | |
| Acetic acid (glacial),100% | + | Cyclohexanone | + | Monochloroacetic acid | + |
| Acetic acid, 96% | + | Cyclopentane | Nitric acid, 10% | + | |
| Acetic anhydride | Decane | + | Nitrobenzene | + | |
| Acetone | + | 1-Decanol | + | Oleic acid | + |
| Acetonitrile | Dibenzyl ether | + | Oxalic acid | + | |
| Acetophenone | Dichloroacetic acid | n-Pentane | |||
| Acetyl chloride | Dichlorobenzene | + | Peracetic acid | ||
| Acetylacetone | + | Dichloroethane | Perchloric acid | + | |
| Acrylic acid | + | Dichloroethylene | Perchloroethylene | ||
| Acrylonitrile | + | Dichloromethane | Petroleum | + | |
| Adipic acid | + | Diesel oil (Heating oil) | Petroleum ether | ||
| Allyl alcohol | + | Diethanolamine | + | Phenol | + |
| Aluminium chloride | + | Diethyl ether | Phenylethanol | + | |
| Amino acids | + | Diethylamine | + | Phenylhydrazine | + |
| Ammonium chloride | + | 1,2 Diethylbenzene | + | Phosphoric acid, 85% | + |
| Ammonium fluoride | + | Diethylene glyco | + | Phosphoric acid, 85% +Sulfuric acid, 95%, 1:1 | |
| Ammonium hydroxide, 30% (Ammonia) | + | Dimethyl sulfoxide(DMSO) | + | Piperidine | + |
| Ammonium sulfate | + | Dimethylaniline | + | Potassium chloride | + |
| n-Amyl acetate | + | Dimethylformamide(DMF) | + | Potassium dichromate | + |
| Amyl alcohol(Pentanol) | + | 1,4 Dioxane | Potassium hydroxide | + | |
| Amyl chloride(Chloropentane) | Diphenyl ether | + | Potassium permanganate | + | |
| Aniline | + | Ethanol | + | Propionic acid | + |
| Barium chloride | + | Ethanolamine | + | Propylene glycol(Propanediol) | + |
| Benzaldehyde | + | Ethyl acetate | Pyridine | + | |
| Benzene (Benzol) | + | Ethyl methyl ketone | + | Pyruvic acid | + |
| Benzine (Gasoline) | Ethylbenzene | Salicylaldehyde | + | ||
| Benzoyl chloride | + | Ethylene chloride | Scintilation fluid | + | |
| Benzyl alcohol | + | Fluoroacetic acid | Silver acetate | + | |
| Benzylamine | + | Formaldehyde, 40% | + | Silver nitrate | + |
| Benzylchloride | + | Formamide | + | Sodium acetate | + |
| Boric acid, 10% | + | Formic acid, 100% | Sodium chloride | + | |
| Bromobenzene | + | Glycerol | Sodium dichromate | + | |
| Bromonaphthalene | + | Glycol(Ethyleneglycol) | + | Sodium fluoride | + |
| Butanediol | + | Glycolic acid, 50% | + | Sodium hydroxide, 30% | + |
| 1-Butanol | + | Heating oil (Diesel oil) | Sodium hypochlorite | + | |
| n-Butyl acetate | + | Heptane | Sulfuric acid, 95% | ||
| Butyl methyl ether | + | Hexane | Tartaric acid | + | |
| Butylamine | + | Hexanoic acid | + | Tetrachloroethylene | |
| Butyric acid | + | Hexanol | + | Tetrahydrofuran (THF) | |
| Calcium carbonate | + | Hydriodic acid | + | Tetramethylammoniumhydroxi de | + |
| Reagent | Compatible | Reagent | Compatible | Reagent | Compatible |
| Calcium chloride | + | Hydrobromic acid | Toluene | ||
| Calcium hydroxide | + | Hydrochloric acid, 20% | + | Trichloroacetic acid | |
| Calcium hypochlorite | + | Hydrogen peroxide,35% | Trichlorobenzene | ||
| Carbon tetrachlorid | Isoamyl alcohol | + | Trichloroethane | ||
| Chloro naphthalene | + | Isobutanol | + | Trichloroethylene | |
| Chloroacetaldehyde,45% | + | Isooctane | Trichlorotrifluoro ethane | ||
| Chloroacetic acid | + | Isopropanol(2-Propanol) | + | Triethanolamine | + |
| Chloroacetone | + | Isopropyl ether | + | Triethylene glycol | + |
| Chlorobenzene | + | Lactic acid | + | Trifluoro ethane | |
| Chlorobutane | + | Methanol | Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) | ||
| Chloroform | Methoxybenzene | + | Turpentine | ||
| Chlorosulfonic acid | Methyl benzoate | + | Urea | + | |
| Chromic acid, 10% | + | Methyl butyl ether | + | Xylene | |
| Chromic acid, 50% | + | Methyl ethyl ketone | Zinc chloride, 10% | + | |
| Chromosulfuric acid | + | Methyl ethyl ketone peroxide | Zinc sulfate, 10% | + | |
| Copper sulfate | + | Methyl formate | + | ||
| Cresol | Methyl propyl ketone | + | |||
| Cumene (Isopropylbenzene) | + | Methylene chloride | |||
| +: There is evidence or it can be concluded with common sense that the chemical can be dispensed with | |||||
| DispensMate; | |||||
| Blank: There is no evidence and it cannot be concluded with common sense that the chemical can be dispensed | |||||
| with DispensMate. If the user tries to use the chemical, DLAB cannot be held responsible for the consequences. | |||||
| Notes: | |||||
| 1 Hydrochloric acid – in the presence of oxidizing may cause slight attack on prolonged boiling. | |||||
| 2 Sulphuric acid – will dull the surface with prolonged heating at above 250°C. | |||||
| 3 Nitric acid (fuming) – may dull the surface with prolonged heating. | |||||
| 4 Phosphoric acid – may dull the surface with prolonged heating. | |||||
| 5 Potassium hydroxide – the fused salt will cause slight attack. | |||||
| 6 Sodium hydroxide – the fused salt will cause slight attack. | |||||
| 7 Hydrogen peroxide 30% – in the presence of hydrochloric acid may cause slight attack on prolonged boiling. | |||||
| 8 Ammonia – heating in an ammonia atmosphere will darken and dull the surface, leading to a porous crystalline | |||||
| appearance. | |||||
| 9 Chlorine – in the presence of hydrochloric acid may cause slight attack on prolonged boiling. | |||||
| 10 Potassium permanganate – in the presence of hydrochloric acid may cause slight attack on prolonged boiling. | |||||
| 11 Sodium carbonate – the fused salt may cause slight attack. | |||||
| 12 Mercury – will readily attack at any temperature. | |||||
| 13 Silver nitrate – the fused salt may cause slight attack and discolor the surface. | |||||
| 14 Organic compounds – there is no data available on most of the organic compounds listed, it is unlikely they | |||||
| would have any detrimental effect but we can give no guarantee to this statement | |||||










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.